Math Series 4
1. Find the first three terms of the Taylor series for f(x) = cos(5x) at x = 0.
- 1 + x - 25 x^2 /2
- 1 - 25x/2 + x^2
- 1 - 25 x^2 /2
- 1 - 25x/2
Answer: C
Solution:
Solution:
Taylor Series:
$$ f(x) = \sum_{k=0}^\infty \frac{(x - x_0)^k}{k!} f^k (x_0) $$ $$\begin{align} x_0 & - \text{ initial guess} \\ f^k & - \text{ kth derivative of $f(x)$ at $X = X_0$} \\ \end{align}$$
@ x 0 = 0,
$$\begin{align}
f(x) & = cos(5x) \to f(0) = 1 \\
f'(x) & = -5 \sin (5x) \to f'(0) = 0 \\
f"(x) & = -25 \cos (5x) \to f"(0) = -25 \\
\end{align}$$
$$\begin{align}
f(x) & = \frac{(x-0)^0}{0!} \cdot 1 + \frac{(x-0)^1}{1!} \cdot 0 + \frac{(x-0)^2}{2!} \cdot (-25) \\
& = 1 - \frac{25}{2}x^2.
\end{align}$$
$$ f(x) = \sum_{k=0}^\infty \frac{(x - x_0)^k}{k!} f^k (x_0) $$ $$\begin{align} x_0 & - \text{ initial guess} \\ f^k & - \text{ kth derivative of $f(x)$ at $X = X_0$} \\ \end{align}$$
2. The first Newton approximation x1 for a zero f(x) = x^3 - 2x with initial approximation x0 = 2.
- 3/5
- 3/7
- 8/7
- 8/5
Answer: D
Solution:
Solution:
Newton-Raphson Method
$$ X_{n+1} = X_n - \frac{Y_n}{Y'_n} $$
Solving for y and y'.
$$\begin{align}
y & = x^3 - 2x \\
y' & = 3x^2 - 2 \\
\end{align}$$
Solving for the 1st iteration at X0 = 2,
$$\begin{align}
X_{n+1} & = X_n - \frac{X_n^3 - 2 X_n}{3X_n^2 - 2} \\
X_1 & = (2) - \frac{2^3 - 2(2)}{3(2)^2 - 2} \\
& = \frac{8}{5} \\
\end{align}$$
$$ X_{n+1} = X_n - \frac{Y_n}{Y'_n} $$
3. Write the converse of the statement, "If Maria Hill finishes her work, she will go to the basketball game."
- If Maria Hill goes to the basketball game, she will not finish her work.
- If Maria Hill goes to the basketball game, she will finish her work.
- If Maria Hill will not go to the basketball game, she will finish her work.
- If Maria Hill will not go to the basketball game, she will not finish her work.
Answer: B
Solution:
Solution:
Implication
$$ p \to q \text{ or "If p, then q."}$$
Converse
$$ q \to p \text{ or "If q, then p."}$$
Inverse
$$ -p \to -q \text{ or "If not p, then not q."}$$
Contrapositive
$$ -q \to -p \text{ or "If not q, then not p."}$$
The converse of the statement "If Maria Hill finishes her work, she will go to the basketball game." is "If Maria Hill goes to the basketball game, she will finish her work."
4. Divide 24 into three parts such that the continued product of the first part, the square of the second part, and the cube of the third part is maximum.
- x = 12, y = 8, z = 4
- x = 14, y = 6, z = 4
- x = 10, y = 8, z = 6
- x = 16, y = 6, z = 2
Answer: A
Solution:
x, y, z as three parts of 24: $$ x + y + z = 24 \text{ (Eq. 1)}$$ Product, $$P = zy^2x^3 \text{ (maximum)}$$
Substuting Eq. 1 to P, $$P = (24-x-y)y^2x^3$$
$$
\frac{\partial P}{\partial x} = \frac d{dx} \left( (24-x-y)y^2x^3 \right) = 0
$$
By subsituting values from choice A and using your calculator, x = 12, y = 8,
$$
\begin{align}
& \begin{array}{c|c}
\frac d{dx} \left[ (24-x-y)y^2x^3 \right] &
_{x=12} \\
& _{y=8} \\
\end{array}\\
& = 0. \\
\end{align}
$$
Solution:
x, y, z as three parts of 24: $$ x + y + z = 24 \text{ (Eq. 1)}$$ Product, $$P = zy^2x^3 \text{ (maximum)}$$
Substuting Eq. 1 to P, $$P = (24-x-y)y^2x^3$$
If the equation of the quantity with unknown max. or min. value have more than two variables, get the partial derivative and equate to zero.
5. What is the integrating factor of the differential equation (1 + x^2)dy/dx + 2xy = cos x ?
- 1 + x2
- 1/(1+x2)
- log (1+x2)
- log (x2)
Answer: A
Solution:
Solution:
1st Order Linear Differential Equation
$$ \frac {dy}{dx} + P(x)y = Q(x) $$
$$ I.F. = e^{\int Pdx}$$
Bernoulli's Differential Equation
$$ \frac {dy}{dx} + P(x)y = Q(x)y^n $$
$$ I.F. = e^{(1-n) \int Pdx}, n \neq 0.1$$
Non-exact Differential Equation
$$ M(x,y)dx + N (x,y)dy = 0, \frac{\partial M}{\partial y} \neq \frac{\partial N}{\partial x} $$
$$ I.F. = e^{\int Pdx}$$
$$ P = \frac{ \frac{\partial M}{\partial y} - \frac{\partial N}{\partial x} }{N}$$
From the given, it can be seen that the D.E. is a 1st Order Linear D.E.:
$$ \begin{align}
(1 + x^2) \frac{dy}{dx} + 2xy & = \cos x \\
\frac{dy}{dx} + \frac{2xy}{1+x^2} & = \frac{\cos x}{1+x^2} \to \text{ 1st Order Linear D.E.} \\
\end{align}
$$
$$
P = \frac{2x}{1+x^2}
$$
$$\begin{align}
I.F. & = e^{\int P dx} \\
& = e^{\int \frac{2x}{1+x^2} dx} \\
\\
\int \frac{du}{u} & = \ln (u) + c \\
u & = 1 + x^2 \\
du & = 2x dx \\
\\
I.F. & = e^{\ln (1+x^2)} \\
& = 1 + x^2.
\end{align} $$
6. The singular point of the differential equation (1-x2) d2y/dx2 - 2x dy/dx + n(n+1)y = 0 is _____.
- x = 0
- x = ±1
- x = 1
- x = 2
Answer: B
Solution:
Solution:
To get the singular point of a D.E., let the term with the highest derivative equal to zero.
Singular Point is the maximum or minimum point and a critical point of 2nd degree D.E. and higher.
From the given, $ (1-x^2) \frac{d^2y}{dx^2} - 2x \frac{dy}{dx} + n (n+1)y = 0$ the term with the highest derivative:
$$\begin{align}
(1-x^2) \frac{d^2y}{dx^2} & = 0 \\
1 - x^2 & = 0 \\
x^2 & = 1 \\
x & = \pm 1 \\
\end{align}$$
7. y = ex is a part of C.F. of differential equation d2y/dx2 + P dy/dx + Qy = 0 if ______.
- 1 + P + Q = 0
- P + Qx = 0
- 1 - P + Q = 0
- P - Qx = 0
Answer: A
Solution:
Solution:
A complementary function is the general solution of homogenous, linear differential equation. Solving the auxiliary equation, gives the value of root m which is needed to find the complementary function. There are three possible complementary solutions (depending on the roots of the auxiliary function):
From the given, the auxiliary equation is:
$$\begin{align}
\frac{d^2 y}{dx^2} + P \frac{dy}{dx} + Qy & = 0 \\
m^2 + P m^1 + Q m^0 & = 0 \\
m^2 + P m + Q & = 0 \\
\end{align}$$
As $y = e^x$ is part of the solution, using Case 1,
$$\begin{align}
e^x & = C_1 e^{mx}\\
x & = m x \\
m & = 1\\
\end{align}$$
Substiuting m,
$$\begin{align}
m^2 + P m + Q & = 0 \\
(1)^2 + P(1) + Q & = 0 \\
1 + P + Q & = 0\\
\end{align}$$
- Case 1: m are real and distinct ($b^2 > 4ac$) $$ y = C_1 e^{m_1 x} + C_2 e^{m_2 x} + ... $$
- Case 2: m are real and equal ($b^2 = 4ac$) $$ y = C_1 e^{m_1 x} + C_2 x e^{m_2 x} $$
- Case 3: m is complex, m = a + bi ($b^2 < 4ac$) $$ y = e^{ax} ( C_1 \cos bx + C_2 \sin bx ) $$
8. The volume of the tetrahedron bounded by the co-ordinate planes and the plane x + y + z = 4 is equal to ____.
- 32/3
- 4/3
- 16/3
- 128/3
Answer: A
Solution:
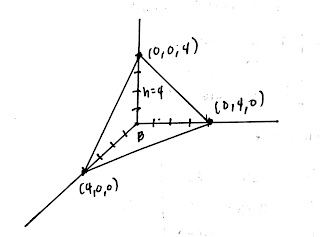
Solution:
$$\begin{align}
V_{(tetrahedron)} & = V_{(pyramid)} \\
& = \frac{1}{3}Bh \\
& = \frac{1}{3} (\frac{1}{2} \cdot 4 \cdot 4) \cdot 4 \\
& = \frac{32}{3}
\end{align}$$

9. The area bounded by the curve xy = 4, y axis, and the lines y = 1 to y = 4 is given by ____.
- 2 log 2
- 8 log 2
- 4 log 2
- 16 log 2
Answer: B
Solution:
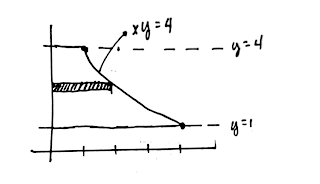
Solution:
$$\begin{align}
Area & =\int_{Y_1}^{Y_2}(X_R - X_L) dy \\
& = \int_1^4(\frac{4}{y}-0) dy \\
& = 8 \ln 2 \\
\end{align}$$

10. If the base radius and height of a cone are measured as 4 and 8 with a possible error of 0.04 and 0.08 inches, respectively, calculate the percentage of error in calculating the volume of the cone.
- 1%
- 3%
- 2%
- 4%
Answer: B
Solution:
Solution:
$$\begin{align}
V_(cone) & = \frac{1}{3}Bh \\
& = \frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h \\
\end{align}$$
initial volume: r = 4, h = 8,
$$\begin{align}
V_i & = \frac{1}{3} \pi (4)^2 (8) \\
& = \frac{128}{3} \pi \\
\end{align}$$
final volume: r = 4 + 0.04, h = 8 + 0.08,
$$\begin{align}
V_f & = \frac{1}{3} \pi (4+0.04)^2 (8+0.08) \\
& = \frac{2060602}{46875} \pi \\
\end{align}$$
$$\begin{align}
\text{% change} & = \frac{V_f - V_i}{V_i} \times 100 \\
& = 3 \% \\
\end{align}$$


Comments
Post a Comment